
Back Verrucomicrobiota German Verrucomicrobiota English Verrucomicrobiota Spanish Verrucomicrobiota French Verrucomicrobiota Portuguese
| Verrucomicrobiota | |
|---|---|
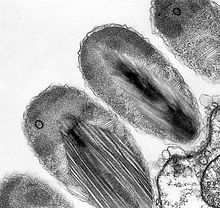
| |
| Transmission electron micrograph of stage II epixenosomes. | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Bacteria |
| Superphylum: | PVC superphylum |
| Phylum: | Verrucomicrobiota Hedlund 2021[1] |
| Classes | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
The phylum Verrucomicrobia is made up of six groups of gram-negative, spherical or rod-shaped bacteria that consume other plants or animals for energy and nutrients (heterotrophic). They are distributed throughout freshwater, marine, and soil habitats, as well as vertebrae digestive tracts including those of humans.[2] The bacteria within this group exist as a free-living organisms or symbiont (organisms that live in close physical association) with eukaryotic hosts from nematode worms and marine sponges to the gut of sea cucumber, clam worm, and humans.[3]
- ↑ Oren A, Garrity GM (2021). "Valid publication of the names of forty-two phyla of prokaryotes". Int J Syst Evol Microbiol. 71 (10): 5056. doi:10.1099/ijsem.0.005056. PMID 34694987. S2CID 239887308.
- ↑ Bergmann, Gaddy T.; Bates, Scott T.; Eilers, Kathryn G.; Lauber, Christian L.; Caporaso, J. Gregory; Walters, William A.; Knight, Rob; Fierer, Noah (2011-07-01). "The under-recognized dominance of Verrucomicrobia in soil bacterial communities". Soil Biology and Biochemistry. 43 (7): 1450–1455. doi:10.1016/j.soilbio.2011.03.012. ISSN 0038-0717. PMC 3260529. PMID 22267877.
- ↑ Cardman, Z.; Arnosti, C.; Durbin, A.; Ziervogel, K.; Cox, C.; Steen, A. D.; Teske, A. (2014-06-15). Spormann, A. M. (ed.). "Verrucomicrobia Are Candidates for Polysaccharide-Degrading Bacterioplankton in an Arctic Fjord of Svalbard". Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 80 (12): 3749–3756. doi:10.1128/AEM.00899-14. ISSN 0099-2240. PMC 4054139. PMID 24727271.
© MMXXIII Rich X Search. We shall prevail. All rights reserved. Rich X Search